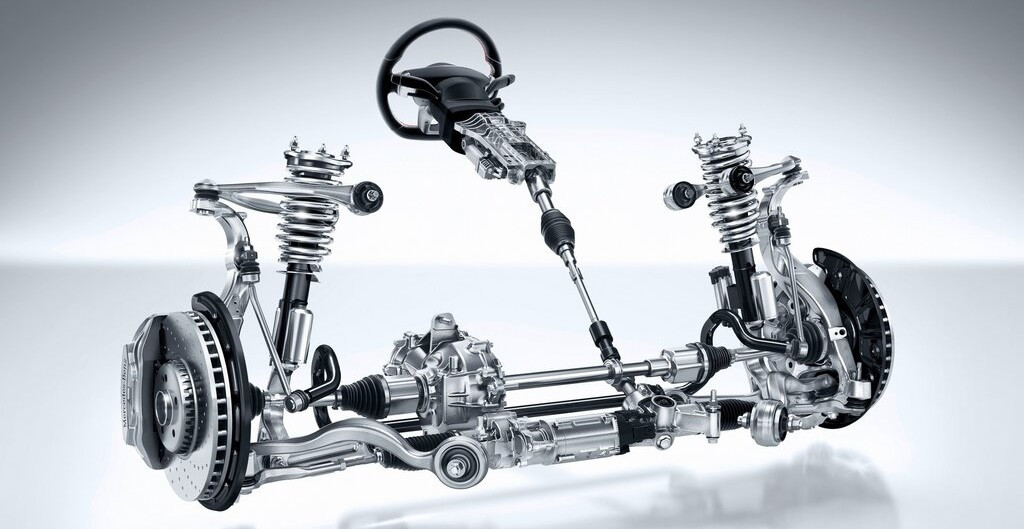
Steering systems are essential components of any vehicle that allow the driver to control the direction of the wheels and the vehicle. There are different types of steering systems, but two of the most common ones are the Parallelogram Steering and the Rack and Pinion Steering. In this article, we will compare and contrast these two systems and explain how they work.
Parallelogram Steering
The Parallelogram Steering is a type of steering system that uses a series of links and arms to steer the vehicle. The main parts of this system are:
- The steering wheel, which is connected to the steering column and the steering gear box.
- The steering gear box, which converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into the linear motion of the pitman arm.
- The pitman arm, which is attached to the steering gear box and the center link.
- The center link, which is a rod that connects the pitman arm and the idler arm.
- The idler arm, which is a support for the center link and is mounted on the opposite side of the chassis.
- The tie rods, which are rods that connect the center link and the steering knuckles.
- The steering knuckles, which are the parts that hold the wheels and allow them to turn.
The Parallelogram Steering works by transmitting the motion of the steering wheel to the wheels through the links and arms. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the steering gear box moves the pitman arm, which in turn moves the center link. The center link then moves the tie rods, which move the steering knuckles and the wheels. The Parallelogram Steering is also known as the conventional steering or the recirculating ball steering.
Rack and Pinion Steering
The Rack and Pinion Steering is a type of steering system that uses a rack and pinion gear set to steer the vehicle. The main parts of this system are:
- The steering wheel, which is connected to the steering column and the pinion gear.
- The pinion gear, which is a small gear that meshes with the rack.
- The rack, which is a long bar with teeth that runs parallel to the front axle.
- The tie rods, which are rods that connect the rack and the steering knuckles.
- The steering knuckles, which are the parts that hold the wheels and allow them to turn.
The Rack and Pinion Steering works by converting the rotational motion of the steering wheel into the linear motion of the rack. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the pinion gear rotates and moves the rack, which in turn moves the tie rods, the steering knuckles, and the wheels. The Rack and Pinion Steering is also known as the direct steering or the simple steering.
Comparison and Contrast
- The Parallelogram Steering and the Rack and Pinion Steering have some similarities and differences. Some of the main points of comparison and contrast are:
- The Parallelogram Steering uses more parts than the Rack and Pinion Steering, which makes it more complex and heavier.
- The Rack and Pinion Steering is more compact and lighter than the Parallelogram Steering, which makes it more suitable for smaller and lighter vehicles.
- The Parallelogram Steering has more joints and connections than the Rack and Pinion Steering, which makes it more prone to wear and tear and requires more maintenance.
- The Rack and Pinion Steering has fewer joints and connections than the Parallelogram Steering, which makes it more durable and requires less maintenance.
- The Parallelogram Steering has more play and backlash than the Rack and Pinion Steering, which makes it less precise and responsive.
- The Rack and Pinion Steering has less play and backlash than the Parallelogram Steering, which makes it more precise and responsive.
Conclusion
The Parallelogram Steering and the Rack and Pinion Steering are two types of steering systems that are used in different types of vehicles. The Parallelogram Steering is more complex, heavier, and less precise than the Rack and Pinion Steering, but it is more suitable for larger and heavier vehicles. The Rack and Pinion Steering is more simple, lighter, and more precise than the Parallelogram Steering, but it is more suitable for smaller and lighter vehicles. Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of the steering system depends on the design and performance of the vehicle.
Comments (0)
Please login to join the discussion
Be the first to comment on this article!
Share your thoughts and start the discussion