Interactive Explorer
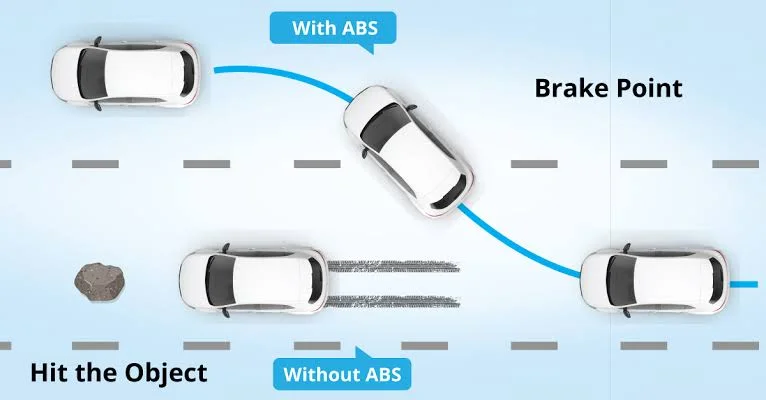
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
The ABS is a critical safety feature that prevents the wheels from locking up during sudden or hard braking. It uses sensors and electronic control to modulate brake pressure, helping the driver maintain steering control. ABS greatly reduces the risk of skidding, especially on wet or slippery roads.
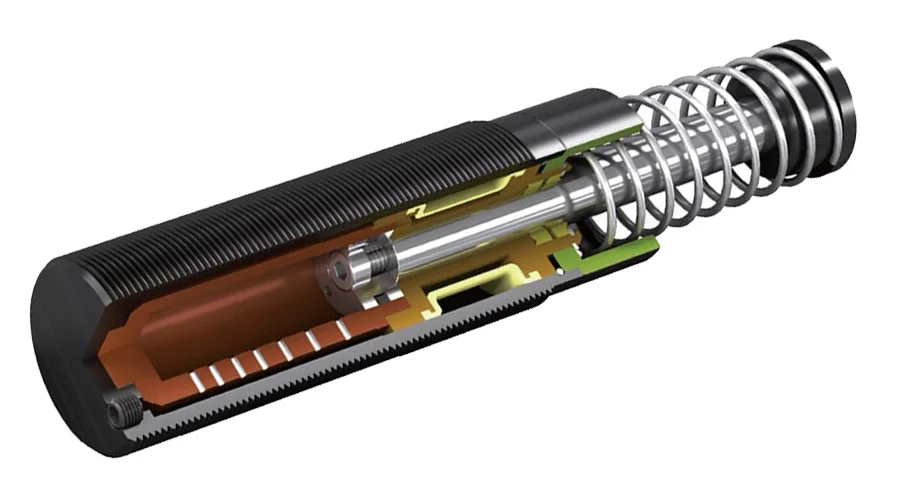

Absorption Shock Absorber (Shock)
A hydraulic device in the suspension system that dampens oscillations and controls the up-and-down movement of the wheels over road irregularities. Shocks contain hydraulic fluid and use valves and pistons to convert kinetic energy from wheel movement into heat energy, providing a smoother ride and maintaining tire contact with the road.
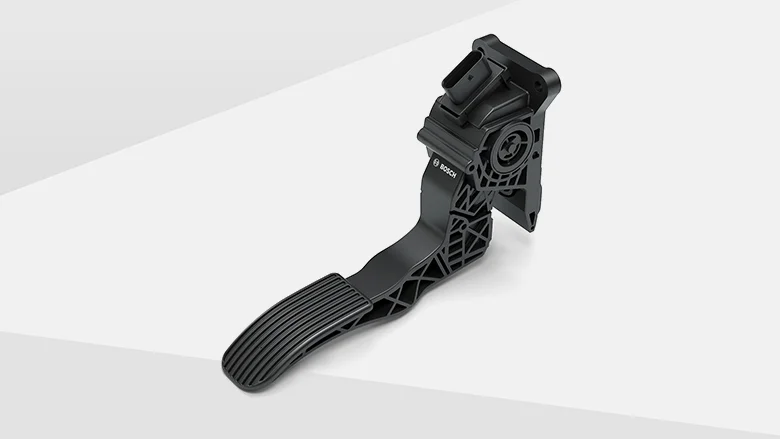

Accelerator (Gas Pedal)
The foot-operated pedal that controls the engine's throttle, regulating the amount of fuel and air mixture entering the engine. Pressing the accelerator increases engine speed and power output, making the vehicle move faster. In electronic throttle systems, the pedal sends signals to the engine control unit rather than operating a mechanical linkage.
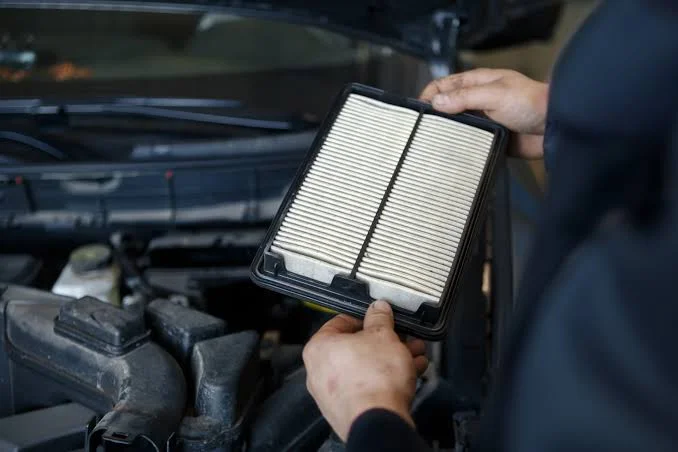

Air Filter
Located in the engine intake system, the air filter cleans the air before it enters the engine for combustion. It traps dust, dirt, and debris to protect the engine's internal parts. A clean air filter ensures better fuel efficiency, improved engine performance, and reduced harmful emissions.
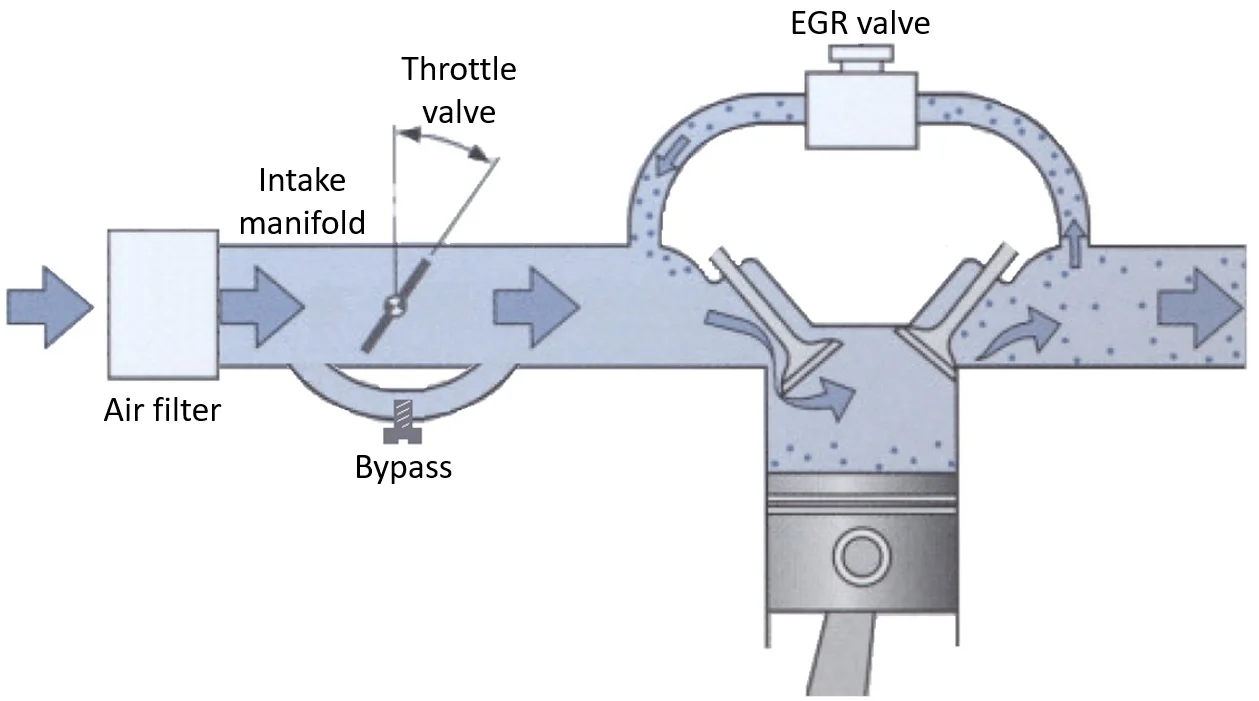
Air Intake System
The network of components that delivers filtered air to the engine for combustion, including the air filter, intake manifold, throttle body, and connecting ducts. The system must provide adequate airflow while filtering contaminants. Performance modifications often focus on improving airflow through this system to increase engine power.
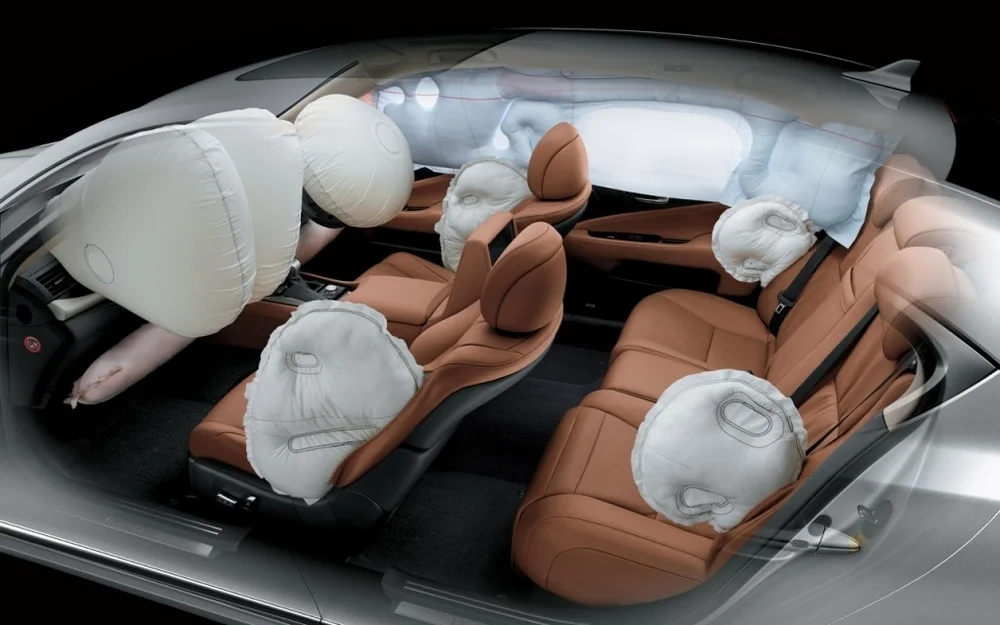

Airbag System
A passive safety system consisting of inflatable cushions designed to protect occupants during collisions. Modern vehicles typically have multiple airbags including front, side, curtain, and knee airbags. The system uses crash sensors to detect impacts and rapidly inflate the bags using a chemical reaction, then quickly deflate to cushion occupants and reduce injury.
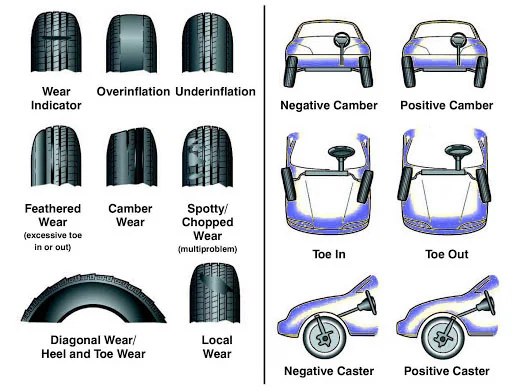
Alignment (Wheel Alignment)
The adjustment of a vehicle's suspension system to ensure that all wheels are positioned correctly relative to each other and the road surface. Proper alignment involves setting the correct angles for camber (wheel tilt), caster (steering axis angle), and toe (wheel direction). Poor alignment causes uneven tire wear, steering problems, and reduced fuel economy.
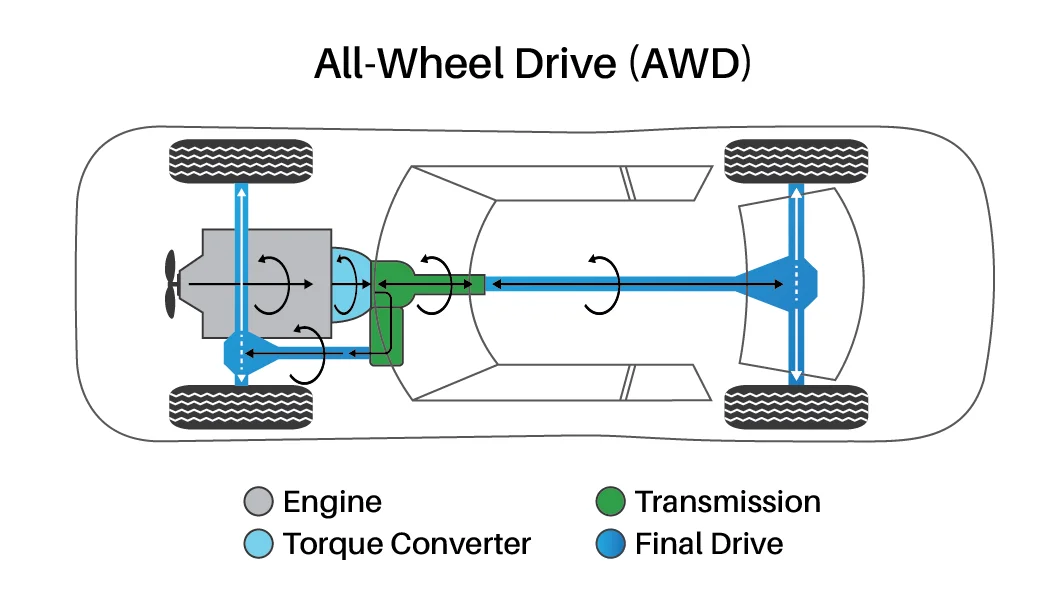
All-Wheel Drive (AWD)
A drivetrain system that automatically distributes engine power to all four wheels as needed, providing improved traction and handling in various road conditions. Unlike 4WD systems, AWD operates continuously without driver input and typically uses a center differential to allow for speed differences between front and rear wheels during normal driving.
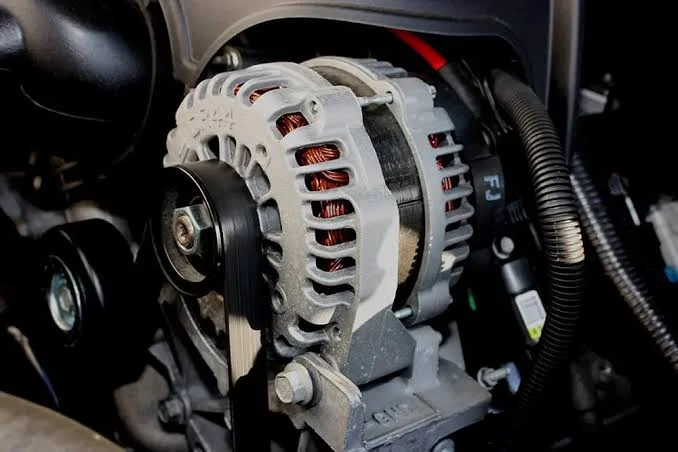

Alternator
The alternator is responsible for generating electricity while the engine runs. It keeps the battery charged and powers essential systems like the lights, dashboard, and infotainment. Without a properly functioning alternator, a vehicle’s battery would quickly lose charge, causing electrical systems to fail.
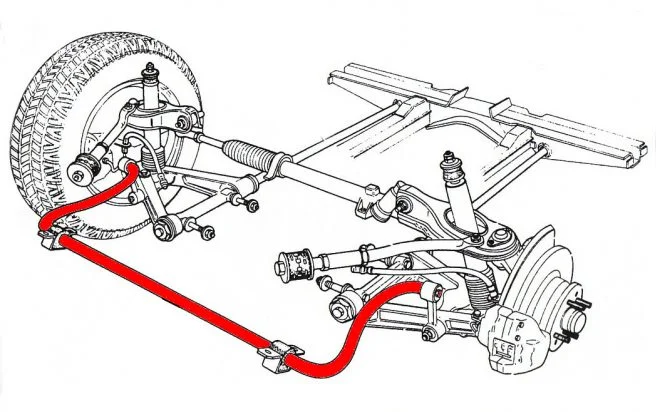
Anti-Roll Bar (Stabilizer Bar)
A metal bar that connects the left and right wheels of the same axle to reduce body roll during cornering. When one wheel encounters a bump or the vehicle turns, the bar transfers some of the force to the opposite wheel, helping maintain vehicle stability and improving handling characteristics. It can be found on front suspension, rear suspension, or both.
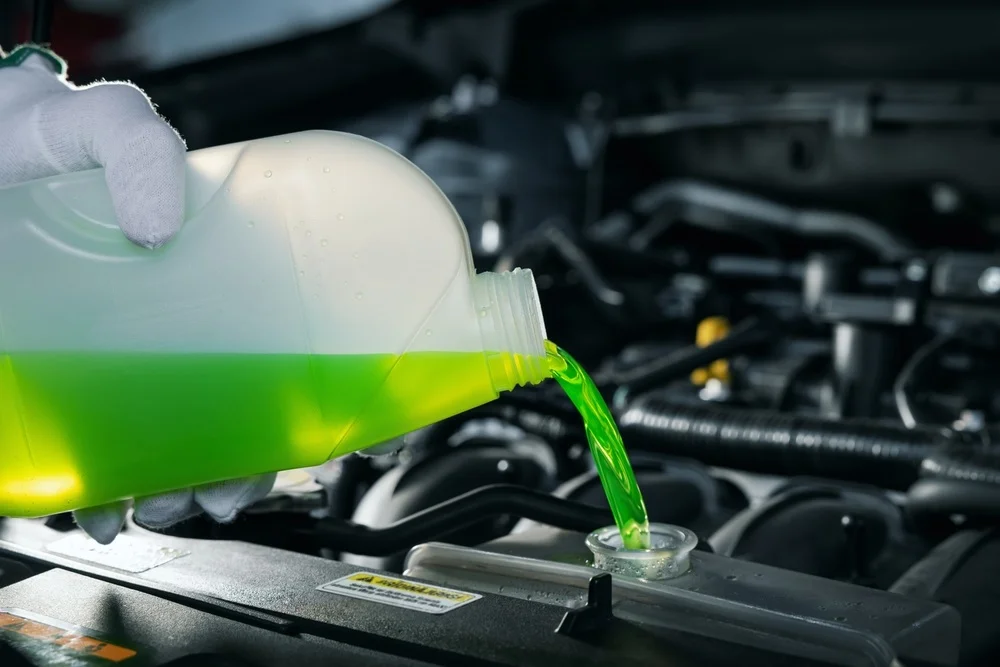

Antifreeze (Coolant)
A chemical mixture, typically containing ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, added to the engine's cooling system to prevent freezing in cold temperatures and overheating in hot conditions. It also contains corrosion inhibitors to protect metal components in the cooling system. Modern antifreeze often comes pre-mixed with water in a 50/50 ratio.
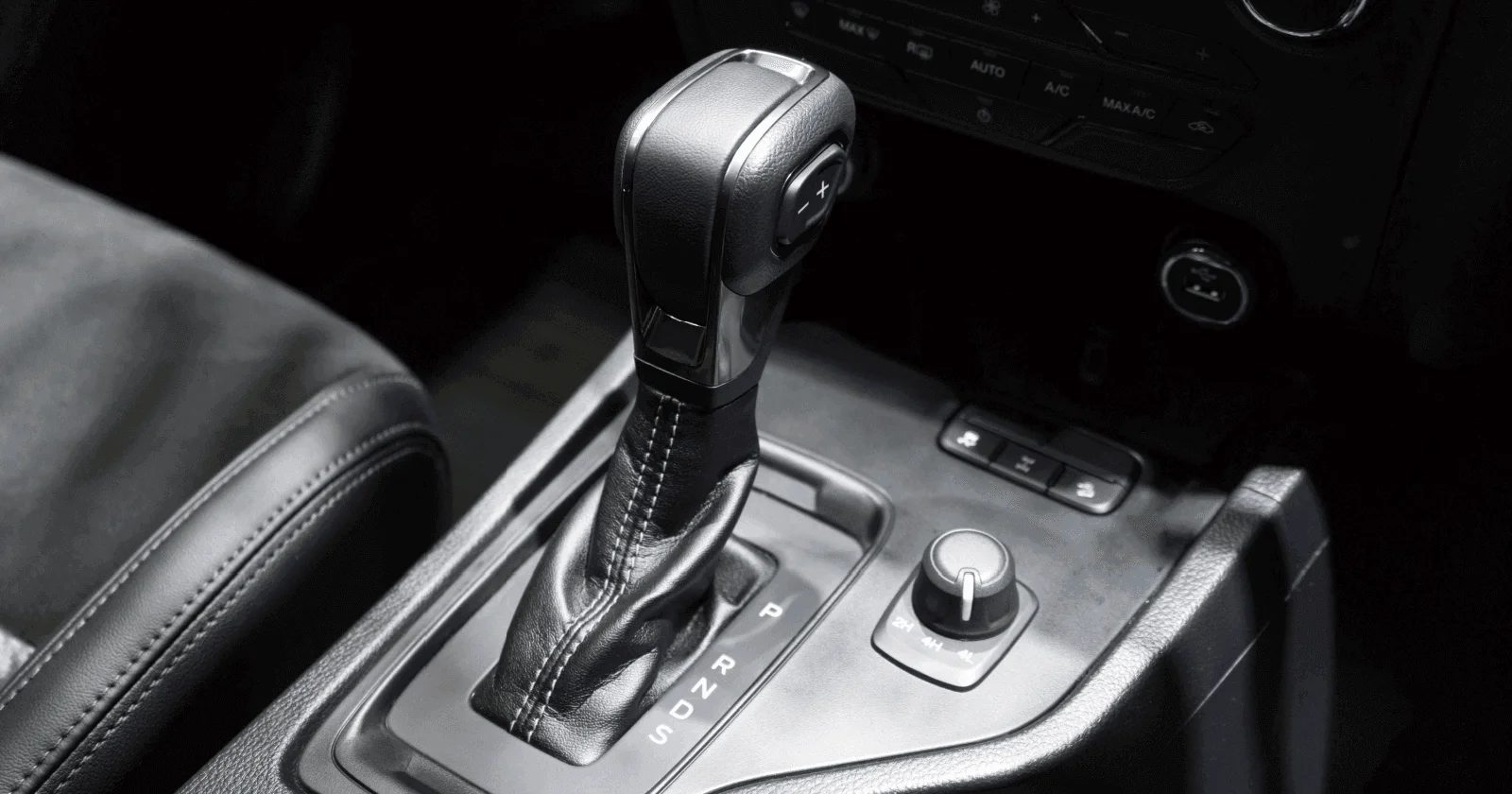

Automatic Transmission
A type of transmission that automatically changes gear ratios as the vehicle moves, freeing the driver from manually shifting gears. It uses a torque converter, planetary gears, and hydraulic controls to select the appropriate gear based on vehicle speed, engine load, and throttle position. This provides smoother acceleration and easier driving compared to manual transmissions.
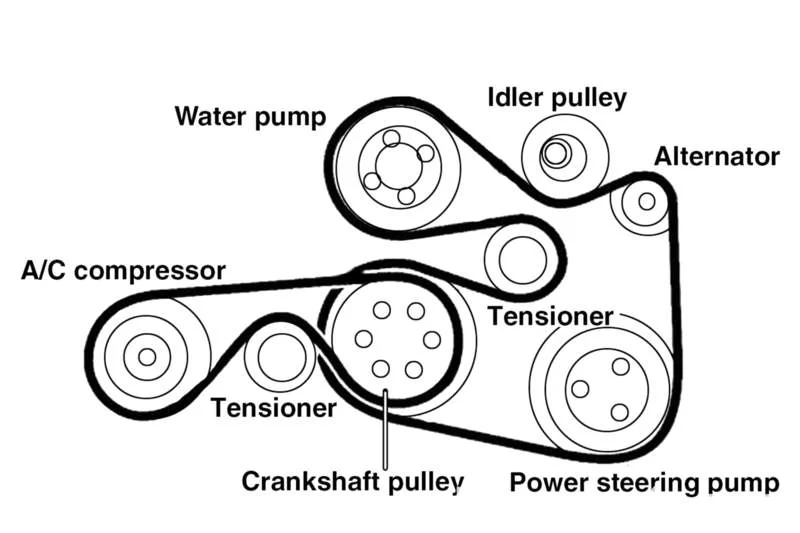
Auxiliary Belt (Serpentine Belt)
A single, continuous belt that drives multiple engine accessories such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. It's called "serpentine" because it winds through various pulleys in a snake-like pattern. Regular inspection and replacement are crucial as belt failure can disable multiple vehicle systems.
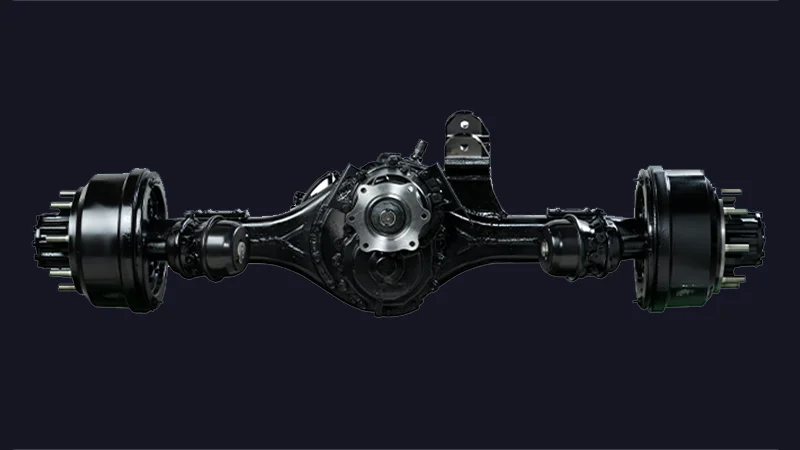

Axle
A central shaft or beam that supports the weight of the vehicle and allows wheels to rotate. There are two main types: drive axles that transmit power from the transmission to the wheels, and non-drive axles that simply support weight. Most vehicles have front and rear axles, with the drive axle(s) depending on whether the vehicle is front-wheel, rear-wheel, or all-wheel drive.